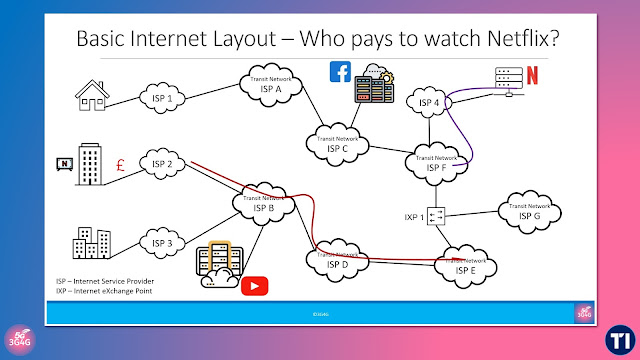
Most people experience the Internet as a seamless service, but beneath that simplicity lies a multi-layered infrastructure made up of interconnected networks, routing policies, exchange points, and edge delivery platforms. These are the systems that keep global data flowing — reliably, efficiently, and at scale.
In our recent explainer video, we examine this invisible architecture by following the path of data from users to content providers and back again. The tutorial covers:
- The hierarchical structure of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and how they form transit chains by purchasing upstream connectivity
- The use of Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) for settlement-free peering between networks, including the difference between public and private peering
- The infrastructure behind Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and the role of Netflix's Open Connect Appliances (OCAs)
- The emerging importance of Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) in localising compute and reducing backbone load
We also touch on real-world examples such as:
- Swisscom’s temporary standoff with Netflix in 2016, highlighting the commercial tensions in peering agreements
- The more recent regulatory intervention by ComCom, requiring Swisscom to establish zero-settlement peering with Init7
These cases demonstrate how infrastructure policy, competitive pressure, and traffic engineering come together to shape the performance and openness of the Internet.
Watch the video below to better understand the physical and logical structures that underpin our digital world:
Whether you're in network planning, architecture, or policy, this video offers a concise look at the building blocks that make the Internet work.
You can download the slides from here.
Related Posts:
- Telecoms Infrastructure Blog: 'Story of the Edge' by Akamai
- Telecoms Infrastructure Blog: The Role of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) in Making Sure Internet Works